What is a non admitted insurance carrier – What is a non-admitted insurance carrier? These companies operate outside the traditional regulatory framework of many states, offering a diverse range of insurance products and posing unique considerations for consumers and businesses. This in-depth exploration delves into the intricacies of non-admitted carriers, highlighting their characteristics, market presence, and the potential benefits and drawbacks for those seeking coverage.
Understanding the differences between admitted and non-admitted carriers is crucial for making informed decisions. Non-admitted carriers often specialize in niche markets or offer products not readily available from traditional insurers, creating a unique landscape within the insurance industry.
Definition and Characteristics
A non-admitted insurance carrier, a vital yet often misunderstood component of the insurance landscape, operates outside the traditional regulatory framework of admitted insurers. They represent a unique alternative for individuals and businesses seeking insurance solutions, navigating a path distinct from those traditionally licensed and regulated by state insurance departments. This alternative model offers a dynamic and sometimes more tailored approach to risk management.These insurers operate independently, often specializing in niche markets or specific types of insurance.
Their independence fosters innovation and agility, yet they face a different set of requirements and responsibilities.
Definition of a Non-Admitted Carrier
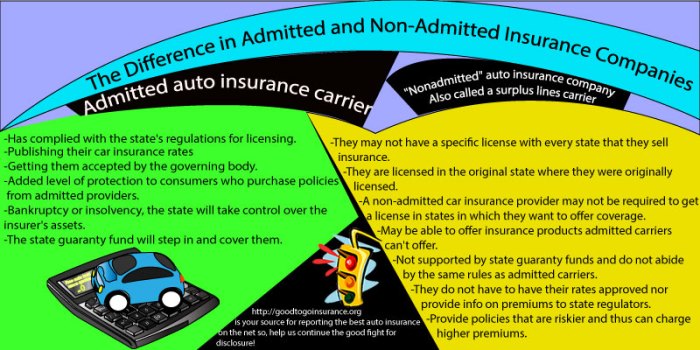
A non-admitted insurance carrier is an insurance company that is not authorized to operate within a particular state’s insurance market. This means they are not licensed or recognized by the state’s insurance regulatory body. Their presence is often determined by the particular insurance needs of a customer base or the specific type of insurance product.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers operate under a different regulatory framework than admitted carriers, which is a key distinction. They typically lack the same level of state oversight and stringent licensing requirements. This difference often reflects a focus on specialized coverage areas or less-regulated lines of insurance. This allows them to offer competitive pricing and unique policy structures.
Implications of Non-Admittance on Operations
The non-admittance status significantly impacts a carrier’s operational structure. Without state licensing, they are excluded from direct access to the state’s insurance market. This necessitates alternative distribution channels and often leads to reliance on intermediaries or agents who are licensed within the state. The lack of direct access to state-regulated financial markets can impact their investment strategies and capital management.
Regulatory Oversight Comparison
Regulatory oversight is a crucial difference between admitted and non-admitted carriers. Admitted carriers are subject to comprehensive state regulation, ensuring policyholders’ protection and fair practices. This scrutiny includes requirements for financial solvency, reserving adequacy, and adherence to established insurance laws. Non-admitted carriers, however, are typically governed by a different regulatory regime, which may be less stringent or focused on different aspects of insurance operations.
Non-admitted insurance carriers aren’t licensed in every state, so you gotta be careful. They might offer cheaper premiums, but they’re not regulated the same way as admitted carriers. This lack of oversight can be a serious problem, especially if you’re dealing with a claim, like with those pesky small brown worms in your house – small brown worms in house.
Basically, they’re a riskier option, so do your homework before you sign on the dotted line. If you’re unsure, stick with a carrier that’s properly licensed in your state.
This difference can be understood as reflecting the need for different oversight structures given the diverse nature of the insurance market.
Licensing Requirements Comparison
Licensing requirements vary substantially between admitted and non-admitted carriers. Admitted carriers must meet strict licensing criteria, including financial strength evaluations, adherence to state insurance laws, and demonstration of adequate capital reserves. Non-admitted carriers, conversely, may not be required to meet the same rigorous standards, but often rely on alternative methods of demonstrating credibility and reliability. These alternative standards may differ depending on the specific insurance product and the carrier’s business model.
The flexibility offered by the absence of direct licensing may attract companies seeking specialized market penetration or unique business opportunities.
Types of Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted insurance carriers, operating outside the regulatory framework of a specific state, present a unique facet of the insurance landscape. These carriers, often specialized in niche markets or offering innovative products, play a significant role in the insurance ecosystem, even though they operate under different regulatory conditions. Understanding their diverse types and offerings is crucial for consumers seeking tailored insurance solutions.
Categorizing Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers fall into various categories, each with distinct characteristics and specializations. Their operational models often center around specific insurance products and target particular customer segments. This categorization provides a structured overview of the different types of non-admitted carriers.
Insurance Products Offered by Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers frequently specialize in specific insurance products, sometimes not offered by admitted carriers. This specialization allows them to cater to unique market demands. Their focus may encompass unusual or niche areas, leveraging their expertise to meet particular customer needs. These products may include specialized insurance solutions, such as those for exotic vehicles or high-value assets.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choice
Several factors influence a consumer’s decision to choose a non-admitted carrier. Cost competitiveness, the unique coverage offered, and the specialized expertise of the carrier often play crucial roles in the decision-making process. The consumer’s particular needs and the insurance product’s characteristics heavily influence the selection process.
Examples of Non-Admitted Carrier Products
Non-admitted carriers frequently handle specialized insurance products. Examples include coverage for high-value assets, rare collectibles, or customized equipment. These types of insurance often require expertise and specific knowledge, which non-admitted carriers may possess. Furthermore, specialized insurance for professional liability or professional errors and omissions is frequently handled by non-admitted carriers.
Table of Non-Admitted Carrier Types
| Carrier Type | Primary Insurance Product | State Regulation Status | Key Market Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialty Underwriters | High-value asset insurance, specialized equipment, exotic vehicles | Not admitted in all states | High-net-worth individuals, businesses with unique assets |
| Reinsurance Companies | Reinsurance for admitted carriers | Often admitted in states where they reinsure admitted carriers | Insurance companies needing to manage risk |
| Direct-to-consumer providers | Specialty insurance products | Not admitted in all states | Specific customer segments |
| Foreign insurers | Various insurance products | Not admitted in some states | Businesses and individuals with international ties |
Market Presence and Competition

Non-admitted insurance carriers carve out a unique space in the competitive landscape, challenging the established norms of the industry. Their presence, often fueled by innovative strategies and a focus on niche markets, significantly impacts the overall insurance market dynamic. Understanding their competitive tactics and their effect on the industry is critical to a comprehensive grasp of the insurance sector.
Competitive Landscape
Non-admitted carriers often operate in specific market segments or with specialized products, allowing them to target underserved customer needs or explore less-saturated areas. This niche focus can lead to a targeted and effective approach, enabling them to compete effectively in specific market segments. They may leverage innovative technologies and streamlined processes to offer competitive pricing and efficient service, potentially attracting customers seeking more affordable options.
Impact on the Overall Insurance Market
The entry of non-admitted carriers introduces a new dimension of competition into the insurance market. This competition fosters a more dynamic environment, potentially driving down premiums and encouraging innovation in product development and service delivery. By offering alternative options, non-admitted carriers can encourage admitted carriers to improve their offerings and adapt to evolving customer demands. The introduction of new players, with their unique approaches, often results in a wider range of choices for consumers.
A non-admitted insurance carrier basically means they aren’t licensed to operate in this particular state. If you’re looking for a home in Brecksville, OH, for example, and are considering insurance options, it’s crucial to check if the carrier is authorized to do business in Ohio, or you might find yourself in a tough spot later. This is something you should definitely consider for any insurance policy, especially when purchasing homes for sale in brecksville oh.
So, be sure to verify the carrier’s licensing before committing. It’s a serious matter when it comes to protecting your investment.
Strategies for Gaining Market Share
Non-admitted carriers employ various strategies to gain and maintain market share. A key strategy often involves specialized product offerings catering to particular needs or risk profiles. Furthermore, cost-effective distribution channels, like online platforms or partnerships with brokers, are utilized to reach consumers efficiently. Direct marketing and targeted advertising campaigns, particularly in online spaces, are employed to attract and retain customers.
Reaching and Engaging Consumers
Non-admitted carriers leverage digital channels to reach and engage consumers. They utilize online platforms to showcase products and provide transparent information. This accessibility, often paired with competitive pricing models, appeals to customers seeking convenient and affordable solutions. Collaborations with brokers and agents provide crucial access points to consumers, especially those who prefer a personalized approach to insurance.
Comparison of Market Share and Strategies
| Carrier Type | Market Share | Marketing Strategy | Competitive Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Admitted Carrier (Example: Specialty Insurer) | Varying, often concentrated in specific niche segments | Niche marketing focusing on particular risks or customer needs; online platforms, targeted advertising; partnerships with specific brokers | Competitive pricing, specialized products, often faster claim processing times in their niche area |
| Admitted Carrier (Example: Large National Insurer) | Significant, broad market presence | Mass marketing, broad distribution network, established brand recognition; often utilize traditional advertising channels | Established brand reputation, extensive network of agents, broader product offerings |
This table illustrates a simplified comparison. Actual market share and strategies can vary significantly depending on the specific carrier and market segment.
Consumer Implications
Navigating the landscape of insurance carriers, particularly non-admitted ones, can feel like charting uncharted waters. Understanding the nuances of dealing with these carriers is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions, ensuring they are well-equipped to protect their interests and financial well-being. A deeper dive into the consumer implications provides a crucial roadmap.Navigating the intricacies of non-admitted insurance carriers can present both opportunities and challenges for consumers.
This section delves into the potential benefits and drawbacks, the safeguards available, and real-world examples to illuminate the path forward.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Dealing with Non-Admitted Carriers
Consumers may find competitive pricing with non-admitted carriers, potentially leading to lower premiums. However, this advantage comes with a trade-off. These carriers often lack the regulatory oversight and financial strength of admitted carriers, posing a risk to consumers regarding claims processing and financial stability. This vulnerability necessitates a cautious approach.
Consumer Protections Available
State insurance departments play a vital role in safeguarding consumers. They often provide information on non-admitted carriers, including their financial stability and claims history. Consumer advocates and organizations can also provide crucial resources and insights into navigating the complexities of non-admitted carriers. Knowing your rights is essential.
Examples of Consumer Experiences with Non-Admitted Carriers
A consumer might find a significantly lower rate with a non-admitted carrier, but when a claim arises, the carrier struggles to process it efficiently. Conversely, a consumer might encounter swift and effective claim settlement, highlighting the varied experiences with these carriers. Each situation presents a unique challenge for consumers to navigate. The key is to research thoroughly.
Importance of Consumer Awareness Regarding Non-Admitted Carriers
Consumers must actively seek information about a non-admitted carrier’s financial strength and claims history before purchasing a policy. This diligence empowers them to make informed choices that align with their needs and risk tolerance. Understanding the regulatory environment is crucial.
Consumer Rights and Responsibilities
| Consumer Right | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Right to Information | Consumers have the right to access clear and concise information about the non-admitted carrier’s financial stability, claims history, and regulatory standing. | Requesting the carrier’s financial statements and claims history from the state insurance department. |
| Right to Fair Treatment | Consumers should expect fair and equitable treatment in all interactions with the carrier, including timely claim processing. | A timely response to a claim inquiry and efficient resolution of a claim. |
| Right to Dispute Resolution | Consumers should have access to formal dispute resolution mechanisms if they have concerns about the carrier’s actions or claim handling. | Utilizing the state insurance department’s complaint procedures or seeking legal counsel. |
| Responsibility to Research | Consumers have the responsibility to thoroughly investigate a non-admitted carrier before purchasing insurance. | Checking the carrier’s financial stability, examining claims history, and understanding the state’s regulatory framework. |
| Responsibility to Understand Policy Terms | Consumers must fully understand the policy’s terms and conditions, including claim procedures. | Carefully reviewing the policy document to understand the scope of coverage and claim handling processes. |
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Navigating the intricate legal landscape surrounding non-admitted insurance carriers is crucial for both the carriers themselves and the consumers they serve. Understanding the regulatory frameworks, compliance requirements, and potential legal pitfalls is paramount for responsible operation and safeguarding consumer interests. This section delves into the vital regulatory aspects, offering a comprehensive overview for a clear understanding of the legal considerations for these carriers.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Non-admitted insurance carriers operate under a complex web of state-specific regulations, often differing significantly from the frameworks governing admitted carriers. These regulations are designed to protect consumers, ensure fair market practices, and maintain the solvency of insurance operations. State insurance departments, wielding substantial authority, oversee the compliance of these carriers within their respective jurisdictions. Their powers encompass licensing, rate approval, and monitoring of financial stability.
Understanding these nuanced state-specific laws is essential for successful navigation.
Compliance Requirements for Non-Admitted Carriers, What is a non admitted insurance carrier
Compliance demands stringent adherence to specific regulations, including licensing requirements, financial reporting, and consumer protection protocols. Non-admitted carriers must demonstrate their financial stability through comprehensive reporting mechanisms, ensuring the safety of their policyholders’ investments. Furthermore, meticulous record-keeping is essential for demonstrating adherence to legal and regulatory guidelines. This includes maintaining detailed records of policyholder information, claims data, and financial transactions.
Effective compliance systems, implemented proactively, are paramount to minimizing the risk of legal challenges.
Potential Legal Challenges Faced by Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers, operating outside the traditional insurance market structures, may face unique legal challenges. Potential disputes might arise from disagreements over policy terms, claims handling procedures, or compliance with state regulations. Furthermore, the lack of direct oversight by a specific state department might increase the complexity of resolving disputes, demanding a heightened level of vigilance and legal expertise.
For instance, challenges regarding jurisdiction, contractual interpretation, or the application of differing state laws can pose significant obstacles.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in Overseeing Non-Admitted Insurance Carriers
Regulatory bodies, such as state insurance departments, play a crucial role in maintaining market stability and consumer protection. Their oversight ensures compliance, manages risks, and fosters fair competition within the non-admitted insurance market. They act as the primary guardians of consumer rights, ensuring fair practices and adequate financial security for policyholders. Their involvement helps to safeguard against fraudulent or unstable carriers, bolstering the overall health of the market.
Key Legal Requirements and Compliance Procedures
| Requirement | Description | Example of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Obtaining and maintaining the necessary licenses in each state where the carrier operates. | Operating without a valid license in a state. |
| Financial Reporting | Submitting accurate and timely financial reports to the state insurance departments. | Failing to submit required financial reports or submitting inaccurate information. |
| Claims Handling Procedures | Adhering to established claims handling procedures Artikeld by state regulations. | Ignoring established claims handling procedures, delaying claim payments, or providing inadequate claim service. |
| Consumer Protection Protocols | Implementing and upholding consumer protection measures as stipulated by the respective states. | Failing to disclose material information to policyholders or refusing to honor policy terms. |
Coverage and Claims Processes
Navigating the intricate landscape of insurance claims with non-admitted carriers requires a keen understanding of their unique procedures. These entities, operating outside the established regulatory framework of admitted carriers, often present distinct challenges and opportunities for both policyholders and claim adjusters. Understanding the claims process for non-admitted carriers is crucial for ensuring a smooth and equitable resolution.The claims process for non-admitted carriers often diverges from the established norms of the admitted market.
Their operational structures, sometimes geographically dispersed, may lead to variations in claims handling procedures. While adhering to contractual obligations, these carriers often utilize specialized tools and techniques to manage claims efficiently, sometimes employing alternative dispute resolution methods. Understanding the potential challenges inherent in these processes is vital to anticipate potential roadblocks.
Claims Handling Procedures
Non-admitted carriers frequently employ a variety of claims handling methods. These may include direct communication with policyholders, using third-party adjusters, or collaborating with local representatives to facilitate the claims process. This often depends on the carrier’s specific structure and the complexity of the claim. The process may vary significantly from one claim to another. A common example might involve a non-admitted auto insurer in a specific state, using local repair shops for damage assessments and settlements, ensuring prompt and efficient resolution within their established protocols.
Methods of Claim Management
Non-admitted carriers employ various strategies for claim management. These strategies may include using advanced software for tracking and processing claims, implementing standardized claim forms, and establishing clear communication channels with policyholders. Some carriers may use risk assessment tools to identify potential claim patterns and adjust their handling approaches accordingly. These methods help to maintain consistency and quality of service, while often relying on streamlined internal processes.
Potential Challenges in the Claims Process
Several potential challenges can arise in the claims process with non-admitted carriers. The lack of regulatory oversight can lead to inconsistencies in claim handling procedures and potential disputes. Policyholders may face difficulties in accessing claim information or contacting the insurer directly, particularly if the insurer operates in a geographically dispersed manner. A lack of established recourse mechanisms may make resolving disputes challenging.
In some cases, the financial stability of the carrier could become a concern, and claims resolution might be delayed or complicated.
Key Steps in a Claims Process for Non-Admitted Carriers
| Step | Description | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Claim Reporting | Policyholder reports the claim to the carrier through designated channels. | Inaccurate or incomplete claim reporting; difficulty in contacting the carrier. |
| 2. Claim Assessment | The carrier assesses the claim’s validity and potential liability. | Discrepancies in assessment methodology; potential delays in evaluation. |
| 3. Evidence Gathering | Relevant evidence, such as documentation, photos, and witness statements, is collected. | Lack of readily available evidence; difficulty in obtaining necessary documentation. |
| 4. Claim Evaluation | The carrier evaluates the claim and determines the appropriate settlement amount. | Disagreements on the value of the claim; variations in evaluation criteria. |
| 5. Settlement Negotiation | The carrier negotiates a settlement with the policyholder. | Difficulty in reaching an agreement; lack of established dispute resolution mechanisms. |
| 6. Claim Closure | The claim is officially closed, and all necessary documentation is finalized. | Incomplete or delayed claim closure procedures; potential for future disputes. |
Insurance Products and Services
Non-admitted insurance carriers, operating outside the traditional regulatory framework, offer a diverse range of products and services, often tailored to niche markets or specific customer needs. Their agility and innovative approach can lead to unique and competitive solutions, but they also come with distinct advantages and disadvantages for consumers. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed decisions in the insurance marketplace.
Types of Insurance Products and Services Offered
Non-admitted carriers frequently provide specialized insurance products, often focusing on areas where traditional insurers have less presence or less competitive pricing. This can include coverage for unusual risks, emerging industries, or specific geographical locations. Their offerings might extend beyond traditional auto, homeowners, and life insurance to encompass specialty areas such as professional liability, surety bonds, or even high-value collectibles insurance.
They also often offer unique policy structures and flexible coverage options.
Advantages of Non-Admitted Carrier Products
Non-admitted carriers can offer competitive premiums and tailored coverage for specific needs. Their flexibility in policy design allows them to respond quickly to market changes and emerging risks. They may cater to customers who have difficulty obtaining coverage from admitted carriers, like those with unusual occupations or high-risk lifestyles. The streamlined process of securing policies can also be an attractive feature for certain clients.
Disadvantages of Non-Admitted Carrier Products
The lack of regulatory oversight can lead to concerns about financial stability and claim handling. Consumers may have limited recourse in the event of a dispute or claim denial, compared to policies issued by admitted carriers. The absence of state-mandated protections might affect consumer confidence and the overall security of their investments.
Examples of Insurance Products and Services
A prominent example is specialized liability coverage for professional consultants, tailored to their specific business risks and potential exposures. Another example is coverage for unique assets like vintage automobiles, with clauses accounting for their high value and specialized maintenance requirements. Additionally, some non-admitted carriers focus on high-risk individuals, offering policies that address unusual situations or lifestyles.
Methods of Promoting Insurance Products
Non-admitted carriers employ various methods to promote their products, including targeted advertising campaigns on specialized industry platforms, partnerships with industry-specific organizations, and collaborations with brokers specializing in niche markets. Direct outreach to potential clients via webinars and online presentations also plays a significant role in reaching a specific audience.
Table of Insurance Products Offered
| Product Type | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Professional Liability Insurance | Covers claims arising from professional negligence or errors in judgment. | Consultants, contractors, architects, and other professionals. |
| Specialty Vehicle Insurance | Covers high-value or unique vehicles, such as vintage cars, motorcycles, and classic trucks. | Collectors, enthusiasts, and owners of valuable vehicles. |
| High-Risk Auto Insurance | Provides coverage for drivers with a history of accidents or violations. | Drivers with poor driving records. |
| Surety Bonds | Guarantees the performance of a contract or obligation. | Businesses and individuals involved in construction, government contracts, or other agreements requiring surety. |
Summary
In conclusion, non-admitted insurance carriers present a distinct alternative in the insurance market, offering both advantages and disadvantages for consumers. Their regulatory status, operational structure, and claim handling procedures differ significantly from admitted carriers. Consumers must be well-informed to navigate the complexities of these alternative providers, prioritizing transparency and understanding potential risks.
Clarifying Questions: What Is A Non Admitted Insurance Carrier
What are the key differences between admitted and non-admitted insurance carriers?
Admitted carriers are licensed and regulated by the state, while non-admitted carriers operate outside this framework. This difference impacts consumer protections, regulatory oversight, and the claims process.
What types of insurance products do non-admitted carriers typically offer?
Non-admitted carriers often specialize in niche markets or offer products not readily available from traditional insurers, such as certain types of specialty insurance or unusual risk exposures.
What consumer protections are available when dealing with a non-admitted carrier?
Consumer protections vary depending on the state and the specific carrier. It’s crucial for consumers to research the specific regulations and protections in their state and for the particular carrier.
What are the potential risks associated with using a non-admitted carrier?
Potential risks include limited consumer protections, varying claim processes, and challenges in enforcing rights in case of disputes.
